TIL
Servlet Authentication Architecture
스프링 시큐리티 주요 아키텍처 컴포넌트
SecurityContextHolder- 스프링 시큐리티가 인증된 사용자를 저장하는 곳
SecurityContextSecurityContextHolder로 접근할 수 있으며 인증한 사용자의Authentication을 가지고 있다.
Authentication- 사용자가 인증을 위해 제공한 credential을 제공하거나
SecurityContext에서 현재 사용자를 제공하기 위한AuthenticationManager에 대한 입력이 될 수 있다.
- 사용자가 인증을 위해 제공한 credential을 제공하거나
GrantedAuthorityAuthentication에서 접근 주체(principal)에 부여한 권한이다.- role, scope 등
AuthenticationManager- 스프링 시큐리티의 필터가 인증을 어떻게 할지 결정하는 API
ProviderManagerAuthenticationManager의 일반적인 구현체
AuthenticationProviderProverManger에 의해 사용되어 특정 타입의 인증을 수행
- Request Credentials with
AuthenticationEntryPoint- 클라이언트에 credential을 요청할 때 사용한다.
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter- 인증에 사용하는 기본
Filter - 여러 컴포넌트를 조합해서 높은 수준의 인증 플로우를 구성할 수 있다.
- 인증에 사용하는 기본
SecurityContextHolder
- 스프링 시큐리티의 중심이 되가는 모델
SecurityContext를 포함하고 있다.
- 인증한 사용자들의 details를 저장하는 곳
- 스프링 시큐리티는
SecurityContextHolder에 어떻게 값이 들어갔는지는 상관하지 않고 값이 있다면 인증된 사용자가 있다고 본다.-
사용자가 인증되었음을 나타내는 가장 쉬운 방법은 직접 값을 넣는 것이다.
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext(); Authentication authentication = new TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER"); context.setAuthentication(authentication); SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context); - 비어 있는 새 컨텍스트를 만드는 것으로 시작한다.
- 스레드 경합을 피하려면
SecurityContextHolder.getContext.setAuthentication()을 사용해선 안 된다.
- 스레드 경합을 피하려면
- 새
Authentication객체를 생성한다.- 프로덕션 환경에선
UserPasswordAuthenticationToken을 주로 사용한다.
- 프로덕션 환경에선
- 마지막으로
SecurityContexHolder에SecurityContext를 설정한다.
-
-
인증된 사용자 정보를 얻으려면
SecurityContextHolder를 통해 접근할 수 있다.SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext(); Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication(); String username = authentication.getName(); Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal(); Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities(); SecurityContextHolder는ThreadLocal에 정보를 저장하기에 동일 스레드라면 항상SecurityContext에 접근할 수 있다.- 요청이 끝나면
FilterChainProxy가 항상ThreadLocal을 비워준다.
- 요청이 끝나면
- ThreadLocal 사용이 적합하지 않은 애플리케이션인 경우 (전체 스레드에서 하나의 컨텍스트를 공유해야 하는 경우) 따로 설정을 할 수 있다.
- 공식 문서 참조
SecurityContext
SecurityContext는Authentication객체를 가지고 있다.
Authentication
Authentication은 다음 2가지 목적으로 제공된다.AuthenticationManager의 입력으로 사용되어 인증된 사용자의 credentials을 제공한다.SecurityContext에서 현재 인증된Authentication을 얻을 수 있다.
Authentication은 다음을 포함한다.principal: 사용자를 나타내며 username/password로 인증했을 시UserDetails인스턴스로 나타난다.credentials: 주로 패스워드이다. 대부분 유츌되지 않도록 인증한 다음 비운다.authorities:GratedAuthority의 추상화로 사용자에게 부여한 권한이다.
GrantedAuthority
- 사용자에게 부여된 권한의 추상화로 role이나 scope를 예로 들 수 있다.
Authentication.getAuthorities()로 얻을 수 있다.GrantedAuthority의Collection이 반환된다.
- 스프링 시큐리티에선 역할(role)을 해석하고 권한을 확인한다.
- username/password 기반 인증이라면 보통
UserDetailsService가GrantedAuthority를 로드한다. - 특정 도메인 객체마다 권한을 부여하지 않고 도메인 객체 단위로 보안 권한을 적용하도록 한다.
- 아니라면 권한을 수천 개 만들어야 할 수도 있다.
AuthenticationManager
- 스프링 시큐리티의 필터들의 인증 수행 방식을 정의하는 API
- 리턴된
Authentication을SecurityContextHolder에 설정하는 건AuthenticationManager를 호출한 객체(시큐리티의 필터)가 담당한다. - 스프링 시큐리티 필터와 통합하지 않는다면
SecurityContextHolder에AuthenticationManager를 거치지 않고Authentication을 직접 설정할 수도 있다. AuthenticationManager의 구현체는 보통ProviderManager이다.
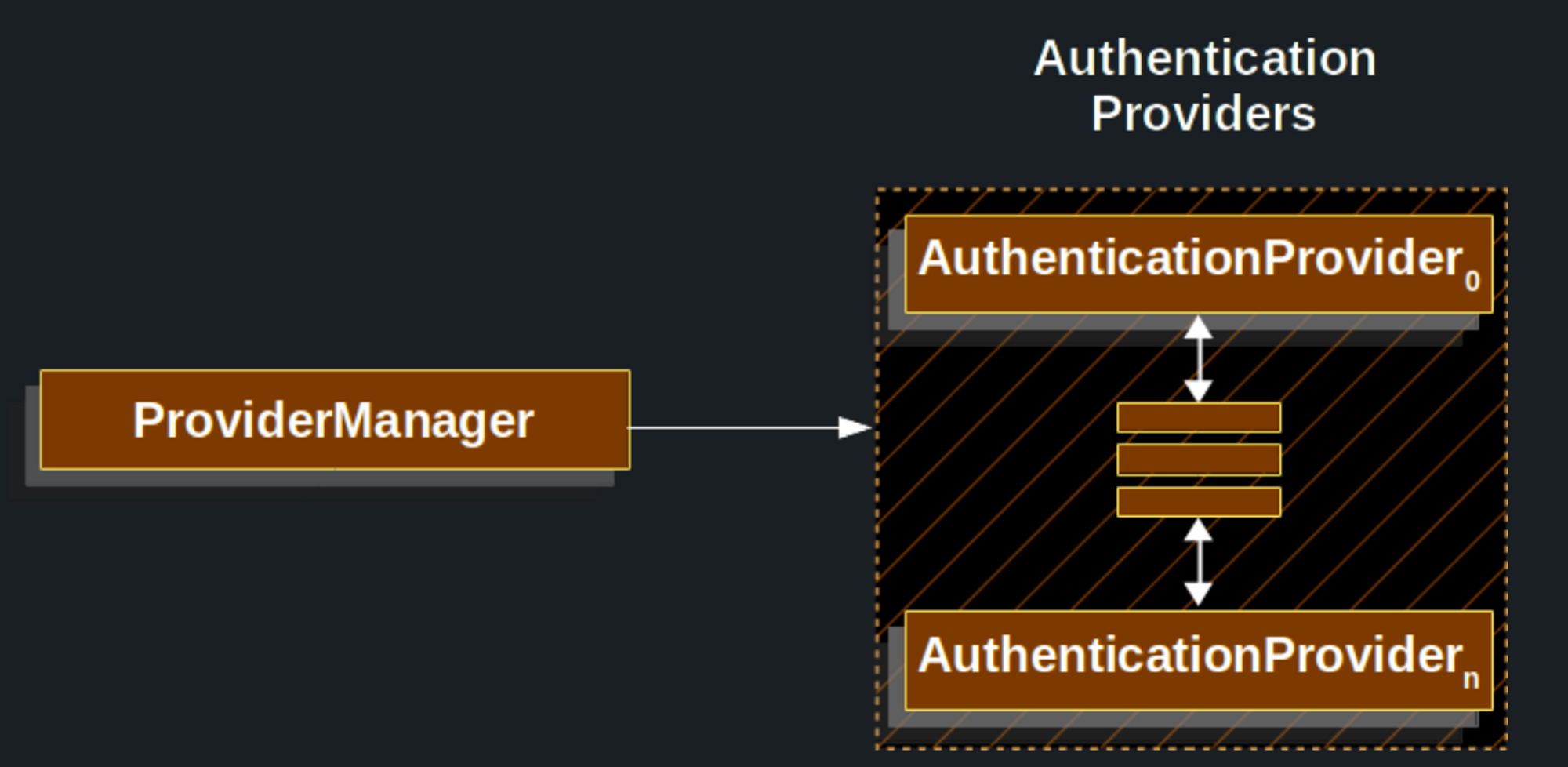
ProviderManager
- 가장 많이 쓰는
AuthenticaitonManager의 구현체 ProviderManager는 동작을AuthenticaitonProvider의List에 위임한다.- 각
AuthenticationProvider는 인증을 성공시키거나 실패시킬 수 있다. - 또 인증 여부를 판단할 수 없다면 다운스트림에 있는
AuthenticationProvider에 결정을 맡긴다. - 모든
AuthenticationProvider가 인증을 판단하지 못하면 특별한 예외인ProviderNotFoundException이 발생한다.
- 각
ProviderFoundException이 발생했다는 뜻은 넘겨진Authentication유형을 지원하는ProviderManager가 설정되지 않았다는 것이다.
- 기본적으로
ProviderManager는 인증에 성공하면 리턴하는Authentication객체에 있는 민감 credential 정보를 지운다.- 비밀번호 등을
HttpSession에 길게 유지하지 않는다.
- 비밀번호 등을
애플리케이션에서 사용자 객체를 캐싱하는 경우
Authentication이 credential을 지워버린다면 캐시된 값으로는 더 이상 인증할 수 없다. 따라서 캐시를 사용한다면 이를 고려하여 구현해야 한다. 객체의 복사본을 만들거나ProviderManager의eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication프로퍼티를 비활성화시켜도 된다.
AuthenticationProvider
ProviderManager에 여러AuthenticationProvider를 주입할 수 있다.- 각
AuthenticationProvider는 특정 유형의 인증을 수행한다. - ex) username/password 인증 방식, JWT 인증 방식 등
- 각
- 따라서 하나의
AuthenticationManager빈만으로 여러 유형의 인증을 모두 처리할 수 있다.ProviderManager가 여러 인증 유형을 지원하는AuthenticationProvider들을 가지고 있기에
Request Credentials with AuthenticationEntryPoint
AuthenticationEntryPoint는 클라이언트에게 credentials을 요청하는 HTTP 응답을 보낼 때 사용한다.- 보통은 클라이언트가 credential을 포함하여 요청을 보내기에 스프링 시큐리티는 위와 같은 응답을 날리지 않는다.
- 클라이언트가 아직 인가되지 않은 리소스에 접근하려할 때 credentials 요청 응답을 보내는 것이다.
- 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉트하거나 WWW-Authenticate 헤더로 응답하거나 한다.
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
AbstractAuthentiationProcessingFilter는 사용자credentials을 인증하는 baseFilter다.- 인증할 수 없다면
AuthenticationEntryPoint가credential요청 응답을 보내는 것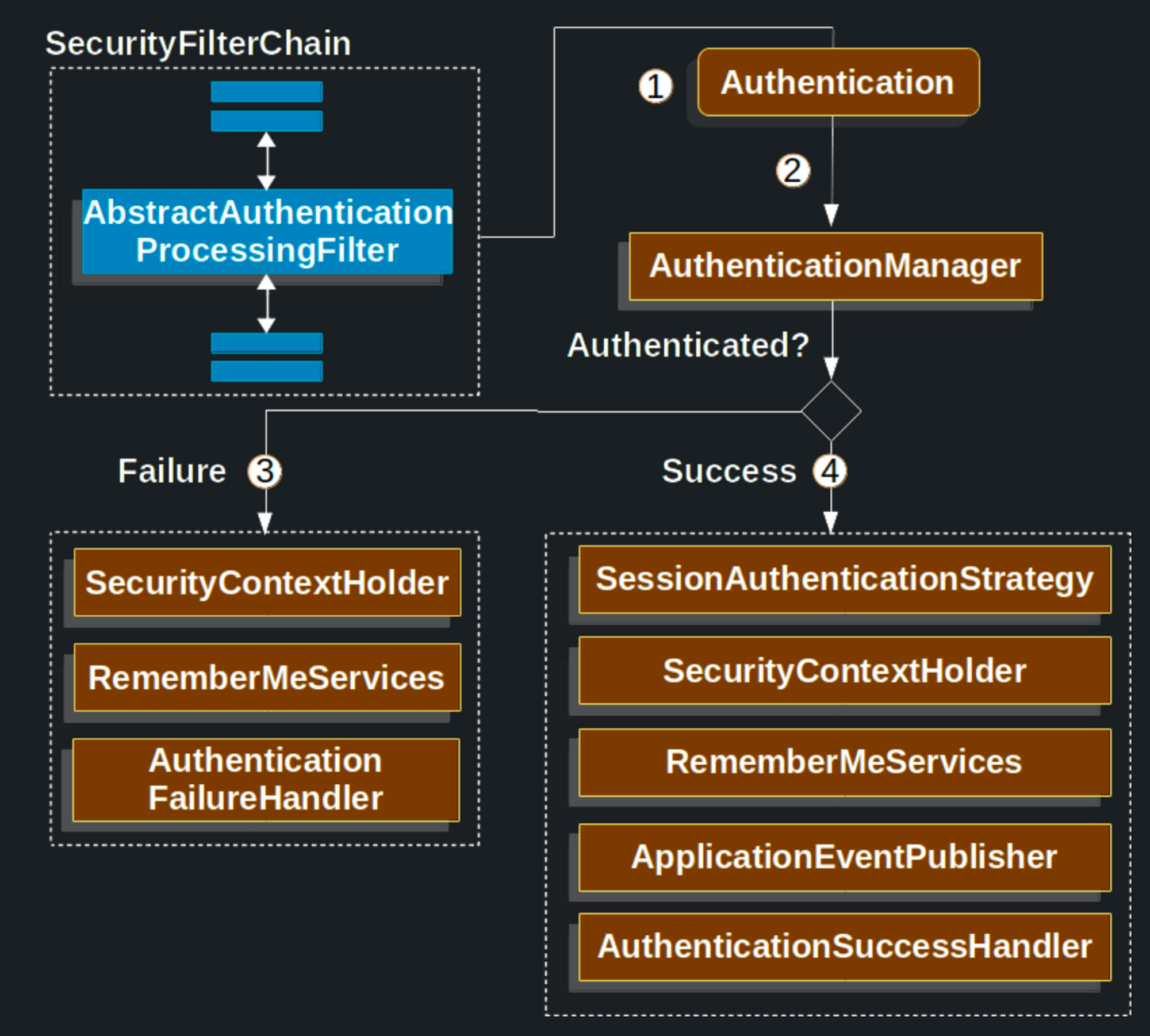 1. 사용자가 credential을 제출하면
1. 사용자가 credential을 제출하면 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFitler가HttpServletRequest에서Authentication을 생성한다.- Authentication의 타입은
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFitler의 하위 클래스에 따라 다르다. - ex)
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter라면UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken타입이 생성된다.Authentication은 인증되기 위해AuthenticationManager에 전달된다.- 인증이 실패하는 경우
SecurityContextHolder가 비워진다.RememberMeServices.loginFial을 실행하는데 remember me를 설정하지 않았다면 동작하지 않는다.AuthenticationFailureHandler가 동작한다.- 인증이 성공하는 경우
SessionAuthenticationStrategy가 새로운 로그인을 통지 받는다.SecurityContextHolder에Authentication이 설정되고SecurityContextPersistenceFilter가SecurityContext를HttpSession에 저장한다.RememberMeServices.loginSuccess가 동작하는데 remember me가 설저오디지 않았다면 동작하지 않는다.ApplicationEventPublisher가InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent를 발행한다.AuthenticationSuccessHandler가 동작한다.
- Authentication의 타입은
- 인증할 수 없다면